🚀 Advanced Elasticity Modeling → XGBoost Regressor
Goal: Model complex, non-linear price elasticity using XGBoost.
Code
# 1️⃣ Load Data import pandas as pd= pd.read_csv('../data/raw/hotel_bookings.csv' )# Filter to completed bookings = df[df['is_canceled' ] == 0 ]# Basic feature engineering 'reservation_status_date' ] = pd.to_datetime(df['reservation_status_date' ])'day_of_week' ] = df['reservation_status_date' ].dt.dayofweek'month' ] = df['reservation_status_date' ].dt.month'stay_length' ] = df['stays_in_weekend_nights' ] + df['stays_in_week_nights' ]# Keep useful columns = df[['adr' , 'lead_time' , 'day_of_week' , 'month' , 'stay_length' , 'market_segment' , 'hotel' ]].copy()
Code
# 2️⃣ Encode categorical features from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder'market_segment_encoded' ] = LabelEncoder().fit_transform(df_model['market_segment' ])'hotel_encoded' ] = LabelEncoder().fit_transform(df_model['hotel' ])
Code
# 3️⃣ Aggregate Bookings by Price & Features # Group data → each row will represent (adr, segment, hotel, etc.) → number of bookings # You can also do this as a time series → here simple aggregate per combination: = df_model.groupby(['adr' , 'market_segment_encoded' , 'hotel_encoded' , 'day_of_week' , 'month' ]) \ = 'bookings' )
0
-6.38
4
1
2
3
1
1
0.00
0
0
1
11
1
2
0.00
0
0
2
6
3
3
0.00
0
0
4
7
1
4
0.00
1
0
0
1
1
Code
# 4️⃣ Train XGBoost Regressor from xgboost import XGBRegressorfrom sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitfrom sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_errorimport numpy as np# Features and target = ['adr' , 'market_segment_encoded' , 'hotel_encoded' , 'day_of_week' , 'month' ]= agg_df[features]= agg_df['bookings' ]# Train/test split = train_test_split(X, y, test_size= 0.2 , random_state= 42 )# Model = XGBRegressor(n_estimators= 500 , learning_rate= 0.05 , max_depth= 5 )# Predict = model.predict(X_test)# Evaluation → safe for all sklearn versions = mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred)= np.sqrt(mse)print (f'RMSE: { rmse:.2f} ' )
Code
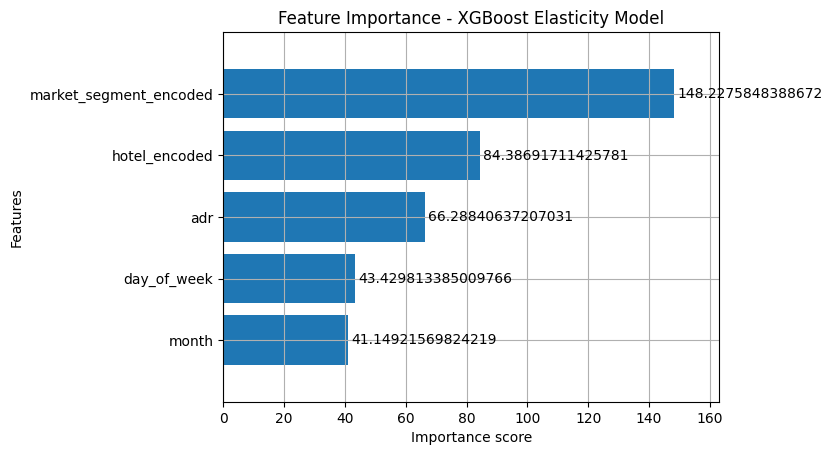
# 5️⃣ Feature Importance → Business friendly import matplotlib.pyplot as pltimport xgboost as xgb= 'gain' , height= 0.8 )'Feature Importance - XGBoost Elasticity Model' )
Code
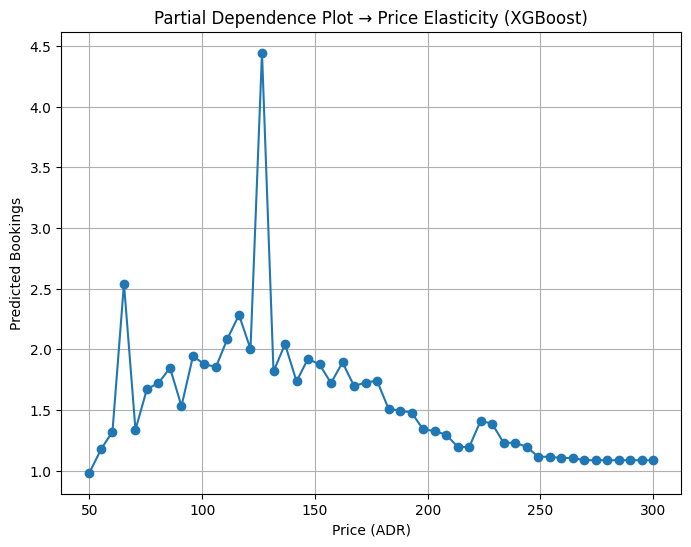
# 6️⃣ Partial Dependence Plot for Price (adr) # Advanced way → use sklearn PartialDependenceDisplay if using sklearn interface # For now → manual simple PDP import numpy as np= np.linspace(50 , 300 , 50 )= []# Fix other features at typical values (e.g., most common segment/hotel, median day/month) = agg_df['market_segment_encoded' ].mode()[0 ]= agg_df['hotel_encoded' ].mode()[0 ]= 3 # mid-week = 6 # summer for adr in adr_values:= pd.DataFrame({'adr' : [adr],'market_segment_encoded' : [default_segment],'hotel_encoded' : [default_hotel],'day_of_week' : [default_day],'month' : [default_month]= model.predict(row)[0 ]# Plot PDP = (8 ,6 ))= 'o' )'Partial Dependence Plot → Price Elasticity (XGBoost)' )'Price (ADR)' )'Predicted Bookings' )